Gum Disease: Causes, Signs & Best Treatments
Did you know that gum disease affects more than half of adults over the age of 30 in the United States? Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common yet often overlooked oral health issue that can have serious consequences if left untreated. From the early stages of gingivitis, characterized by red and swollen gums, to the advanced periodontitis that can lead to tooth loss, understanding the causes, signs, and best treatments for gum disease is crucial for maintaining healthy gums and overall oral health.
Key Takeaways:
- Gum disease affects over half of adults over the age of 30 in the US.
- Proper oral hygiene is crucial in preventing gum disease.
- Gingivitis is the early stage of gum disease and is characterized by red and swollen gums.
- Periodontitis is an advanced form of gum disease that can lead to tooth loss.
- Effective treatments for gum disease include deep cleaning, antibiotic therapy, and surgical procedures.
Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It is characterized by inflammation, infection, and eventual damage to the gum tissues and bone surrounding the teeth.
Gum health plays a crucial role in maintaining overall oral hygiene. When gums are healthy, they act as a protective barrier against harmful bacteria and plaque buildup. However, poor oral hygiene practices can lead to the development of gum disease.
Proper oral hygiene is essential in preventing the onset and progression of gum disease. Regular brushing, flossing, and rinsing with mouthwash help remove plaque and food particles, reducing the risk of gum inflammation and infection.
Gum disease progresses through various stages, starting with gingivitis and advancing to periodontitis. Gingivitis is the early stage of gum disease characterized by redness, swelling, and bleeding gums. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, where the gum tissues pull away from the teeth, leading to receding gums, loose teeth, and potential tooth loss.
| Type of Gum Disease | Description |
|---|---|
| Gingivitis | The early stage of gum disease, characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. |
| Periodontitis | Advanced gum disease that involves the destruction of the gum tissues and bone surrounding the teeth. |
Detecting gum disease in its early stages is crucial for effective treatment. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings allow dentists to assess and monitor gum health. By promptly identifying and addressing any signs of gum disease, individuals can prevent further damage to their oral health.
In the next section, we will discuss the signs and symptoms that indicate the presence of gum disease, helping individuals recognize and seek appropriate treatment for this common oral health condition.
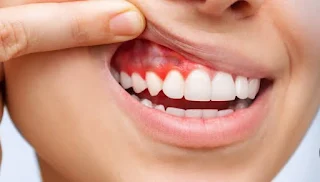
Signs and Symptoms of Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common dental ailment that affects many individuals. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of gum disease is crucial in order to seek timely treatment and prevent further complications.
One of the early stages of gum disease is gingivitis, which is characterized by:
- Redness and inflammation of the gums
- Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to a more advanced stage known as periodontitis, which involves:
- Receding gums
- Loose teeth or tooth loss
- Persistent bad breath
Another common symptom of gum disease is swollen gums, which can be tender and painful to touch. Swollen gums are often a sign of inflammation caused by the buildup of plaque and bacteria along the gumline.
If you experience any of these signs and symptoms, it is essential to schedule an appointment with your dentist as soon as possible for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Comparison of Gingivitis and Periodontitis Symptoms
| Gingivitis Symptoms | Periodontitis Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Red and inflamed gums | Receding gums |
| Bleeding gums | Loose teeth or tooth loss |
| Persistent bad breath |
Causes of Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is primarily caused by poor oral hygiene and lack of regular dental care. Maintaining proper oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing and flossing, is crucial in preventing gum disease. When plaque and bacteria are not adequately removed from the teeth and gums, they can lead to gum inflammation and infection.
Other factors that contribute to gum disease include:
- Smoking: Tobacco use increases the risk of gum disease and can hinder the healing process.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can make gums more susceptible to infection.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as certain anticonvulsants and immunosuppressants, can affect gum health.
- Genetic predisposition: Some individuals may be genetically more prone to developing gum disease.
While these factors can increase the risk of gum disease, maintaining a thorough oral hygiene routine and regular dental check-ups can help prevent its development. It is essential to prioritize oral health and seek professional dental care to reduce the likelihood of gum disease.
"Preventing gum disease starts with proper oral hygiene and regular dental care. By taking these steps, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing gum disease and maintain optimal gum health."
| Causes of Gum Disease | Preventive Measures |
|---|---|
| Poor oral hygiene | Regular brushing and flossing |
| Smoking | Avoid tobacco products |
| Hormonal changes | Maintain good oral hygiene during hormonal fluctuations |
| Certain medications | Inform your dentist of any medications you are taking |
| Genetic predisposition | Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings |
Diagnosing Gum Disease
When it comes to gum disease, early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Dentists employ various methods to accurately assess the severity of gum disease, including gingivitis and periodontitis. These diagnostic techniques help evaluate the extent of inflammation, identify potential areas of concern, and guide appropriate treatment plans for patients.
Gingivitis Evaluation
Dentists first perform a visual examination of the gums to identify signs of gingivitis, the early stage of gum disease. They check for redness, swelling, and any bleeding during gentle probing. Dentists may also use a periodontal probe, a slender instrument, to measure the depth of the pockets around the teeth. Increased pocket depth indicates gum inflammation and possible progression to periodontitis.
Periodontitis Assessment
For a more detailed evaluation, dentists may request dental X-rays to assess the condition of the supporting bone structure and identify any signs of bone loss due to periodontitis. They carefully analyze these X-rays to determine the extent of damage and plan appropriate treatment. Through these diagnostic measures, dentists can accurately classify gum disease and develop a customized treatment plan based on the individual's needs.
Early diagnosis plays a pivotal role in successful management of gum disease. Regular dental check-ups and professional evaluations are essential in identifying gum disease at its earliest stages, allowing for timely interventions to prevent further complications. Don't ignore the signs—seek professional help to protect your oral health.
| Diagnostics Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Visual Examination | A comprehensive evaluation of the gums to identify visible signs of gingivitis and periodontitis, such as redness, swelling, and bleeding. |
| Probing | Assessment of gum health through gentle probing with a periodontal probe, measuring pocket depth to detect signs of gum inflammation and possible progression to periodontitis. |
| Dental X-rays | Utilization of X-rays to examine the supporting bone structure around the teeth. This aids in evaluating the integrity of the bone and identifying any signs of bone loss caused by periodontitis. |
Treatment Options for Gum Disease
Treating gum disease is crucial to prevent further complications and maintain oral health. There are a variety of treatment options available, ranging from non-surgical interventions to more invasive procedures. Your dentist will determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the severity of your gum disease.
Non-Surgical Treatments
The initial stage of gum disease, known as gingivitis, can often be treated with non-surgical methods. These treatments aim to reduce inflammation and remove plaque and tartar buildup.
- Professional dental cleaning: Your dentist or dental hygienist will perform a thorough cleaning of your teeth, removing plaque and tartar above and below the gumline.
- Scaling and root planing: This deeper cleaning procedure involves removing plaque and tartar from the roots of your teeth and smoothing the tooth surfaces to prevent further buildup.
- Antibiotic therapy: Antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate bacteria and control infection in the gums. These may be in the form of mouth rinses, gels, or oral tablets.
Surgical Treatments
If gum disease has advanced to a more severe stage, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical treatments aim to repair damaged gum tissue, regenerate bone, and restore oral health.
- Gum grafting: This procedure involves taking tissue from another part of your mouth and attaching it to the affected area to replace receded gum tissue.
- Flap surgery: Also known as pocket reduction surgery, flap surgery involves lifting the gums to remove tartar and bacteria from deep pockets, and then securing the gums back in place to promote proper healing.
- Bone grafting: In cases where gum disease has caused bone loss, bone grafting may be necessary to regenerate bone tissue and provide support for the teeth.
During and after treatment, it is essential to maintain good oral hygiene practices to prevent the recurrence of gum disease. This includes regular brushing, flossing, and using an antibacterial mouthwash. Your dentist may also recommend follow-up appointments to monitor your progress and ensure the effectiveness of the treatment.
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Professional Dental Cleaning | Thorough removal of plaque and tartar above and below the gumline |
| Scaling and Root Planing | Deep cleaning of the roots of your teeth and smoothing of tooth surfaces |
| Antibiotic Therapy | Prescription of antibiotics to control infection and eliminate bacteria |
| Gum Grafting | Transfer of tissue from another part of your mouth to replace receded gum tissue |
| Flap Surgery | Lifting of the gums to remove tartar and bacteria, followed by secure reattachment |
| Bone Grafting | Regeneration of bone tissue to provide support for the teeth |
Preventing Gum Disease
Prevention is key when it comes to gum disease. By following a few simple steps, you can reduce your risk and maintain optimal oral health. Here are some practical tips to help you prevent gum disease:
- Practice good oral hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste, using a soft-bristled toothbrush. Pay special attention to the gumline where bacteria tend to accumulate. Don't forget to replace your toothbrush every three to four months.
- Floss daily: Regular flossing removes plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gumline, preventing the development of gum disease. Be gentle when flossing to avoid causing damage to your gums.
- Use mouthwash: Rinse your mouth with an antimicrobial mouthwash after brushing and flossing. This helps reduce plaque and kills bacteria that can lead to gum disease.
- Visit your dentist regularly: Schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings to ensure early detection and timely treatment of any gum-related issues. Your dentist can identify signs of gum disease in its early stages and provide appropriate guidance.
- Eat a balanced diet: Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in maintaining gum health. Include foods rich in vitamins and minerals, such as fruits and vegetables, and limit your consumption of sugary snacks and beverages.
- Avoid tobacco products: Smoking and chewing tobacco not only stain your teeth but also significantly increase your risk of developing gum disease. Quitting or avoiding these products can greatly improve your gum health.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress weakens your immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off infections, including gum disease. Incorporate stress management techniques into your daily routine, such as exercise, meditation, or engaging in hobbies.
By implementing these preventive measures and maintaining a consistent oral care routine, you can significantly reduce your risk of gum disease. Remember, prevention is always better than cure when it comes to your oral health.
Maintaining Gum Health
To ensure optimal oral health, maintaining gum health is crucial. Healthy gums are an integral part of a strong foundation for your teeth, providing support and protection against gum disease. By following these essential steps, you can keep your gums in excellent condition:
1. Practice Good Oral Hygiene
Proper oral hygiene is vital for maintaining gum health. Brush your teeth twice a day for at least two minutes each time, using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Don't forget to clean your tongue to remove bacteria that can cause gum problems. Floss daily to remove plaque and food debris from between your teeth, reaching areas that your toothbrush can't access. Rinse with an antimicrobial mouthwash to kill any remaining bacteria and freshen your breath.
2. Follow a Balanced Diet
A healthy diet plays a significant role in gum health. Include foods rich in vitamins and minerals, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy products. Avoid excessive consumption of sugary and acidic foods and beverages, as they can contribute to gum inflammation and decay. Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and wash away food particles.
3. Quit Tobacco Products
Smoking and using other tobacco products are known to have detrimental effects on gum health. These habits weaken the immune system and restrict blood flow to the gums, making them more susceptible to infection and disease. Quitting tobacco products can significantly improve your gum health and overall oral well-being.
4. Manage Stress
Stress can have negative implications for your oral health, including your gums. When you're under stress, your immune system may be compromised, making it harder for your body to fight off gum infections. Finding healthy coping mechanisms, such as practicing relaxation techniques, regular exercise, and getting enough sleep, can help manage stress and protect your gum health.
By implementing these strategies, you can maintain gum health and prevent gum disease. Remember to visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and check-ups to ensure the early detection and treatment of any potential gum issues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gum disease is a common oral health issue that requires attention and proper care. Throughout this article, we have explored the causes, signs, and best treatments for gum disease. It is crucial to understand that early detection is key to preventing the progression of gum disease. Regular dental check-ups and maintaining a good oral hygiene routine are essential in this regard.
By practicing daily brushing and flossing, individuals can effectively reduce the risk of gum disease. Moreover, incorporating mouthwash into their oral hygiene routine can further promote gum health. However, it is important to note that if any signs or symptoms of gum disease arise, seeking professional dental assistance is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Remember, gum disease can lead to serious complications if left untreated, including tooth loss and systemic health issues. Taking proactive measures to prevent gum disease is vital for maintaining a healthy smile and overall well-being. Stay vigilant, prioritize your gum health, and partner with your dentist to achieve optimal oral health.
FAQ
What is gum disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, refers to an infection that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth, including the gums and jawbone. It is typically caused by the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, on the teeth and gums. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to serious oral health problems and even tooth loss.
What are the signs and symptoms of gum disease?
The signs and symptoms of gum disease can vary depending on the stage and severity of the condition. Common indicators include red, swollen, and tender gums, bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, receding gums, loose teeth, and changes in the bite. It's important to consult a dentist if any of these symptoms are present.
How can gum disease be prevented?
Preventing gum disease involves maintaining good oral hygiene practices. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing daily, using mouthwash, and visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups and professional cleanings. Additionally, avoiding tobacco products, maintaining a balanced diet, and managing stress can contribute to gum health and overall oral hygiene.
What are the treatment options for gum disease?
The treatment options for gum disease depend on the stage and severity of the condition. Non-surgical treatments may include deep cleaning procedures called scaling and root planing, antibiotic therapy, and antimicrobial mouth rinses. In more advanced cases, surgical interventions such as gum grafting and flap surgery may be necessary. It is important to consult a dental professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
How is gum disease diagnosed?
Dentists typically diagnose gum disease through a comprehensive dental examination. This may involve visually inspecting the gums for signs of inflammation, measuring the depth of gum pockets using a periodontal probe, and taking dental X-rays to assess the extent of jawbone damage. Early detection and regular dental check-ups are crucial in diagnosing and treating gum disease.


.jpg)

0 Comments